Carbon Capture: A Promising Path to Reducing Corporate Carbon Footprints?
As the global community grapples with the urgent need to address climate change, businesses around the world are exploring innovative solutions to reduce their carbon footprints. One such technology is carbon capture, which has the potential to revolutionize how we mitigate the effects of greenhouse gas emissions.
But what is carbon capture, how does it work, and to what extent can companies use it to reduce their carbon footprint?
Understanding Carbon Capture:
Carbon capture, also known as carbon capture and storage (CCS), is an innovative technology that seeks to remove carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere, either from industrial and energy-related sources or directly from the air. The captured CO2 is then transported and stored deep underground in geological formations, such as depleted oil and gas reservoirs or saline aquifers, where it is securely contained.
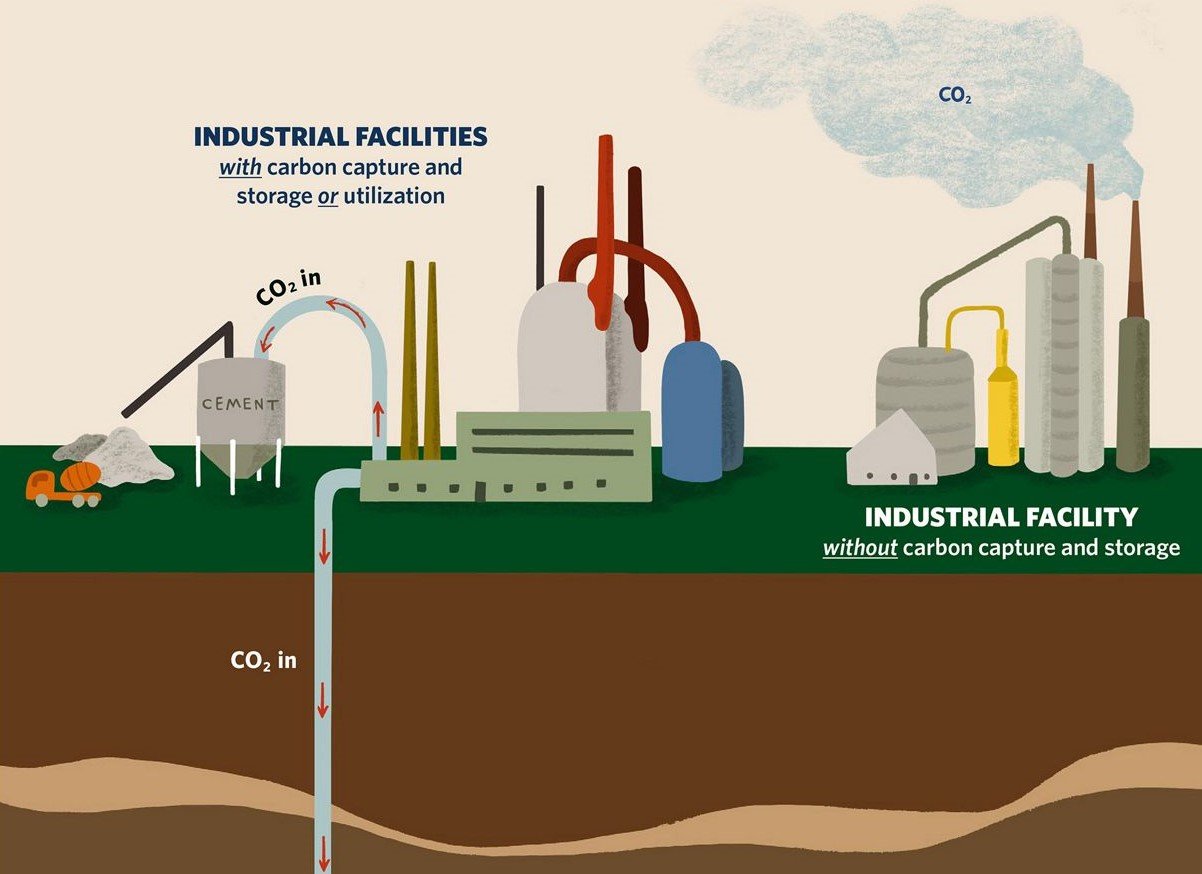
The process of carbon capture
One method is illustrated here.
Capture: CO2 is separated from other gases produced during combustion or industrial processes. This can be done using various technologies, such as absorption, adsorption, or membrane separation.
Transportation: Once captured, the CO2 is compressed and transported, usually via pipelines, to a suitable storage site.
Storage: The compressed CO2 is then injected deep underground, typically into porous rock formations, such as depleted oil and gas reservoirs or deep saline aquifers. These formations are chosen because they have natural barriers, like layers of impermeable rock, that prevent the CO2 from escaping back into the atmosphere.
Capturing Carbon for Businesses:
For companies, carbon capture can yield significant emission reductions and accelerate the transition towards a low-carbon economy. This is particularly relevant for hard-to-decarbonize sectors like cement, steel, and aviation, which have limited options for emission reductions. Furthermore, carbon capture can complement renewable energy sources, ensuring a more sustainable and reliable energy mix for businesses across all industries.
Challenges:
Despite its promise, carbon capture faces several challenges. High implementation costs and limited public awareness may hinder large-scale adaption. Additionally, some critics question the effectiveness and longevity of the method and claim that it would distract from the actual goal. Companies could face criticism from customers or investors. Consequently, there is a need for more research. Although carbon capture technology has come a long way, it is still evolving. Current CCT methods may not be suitable for all industries or may not capture CO2 as efficiently as desired.
To overcome these obstacles, businesses can invest in research and development to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of CCS.